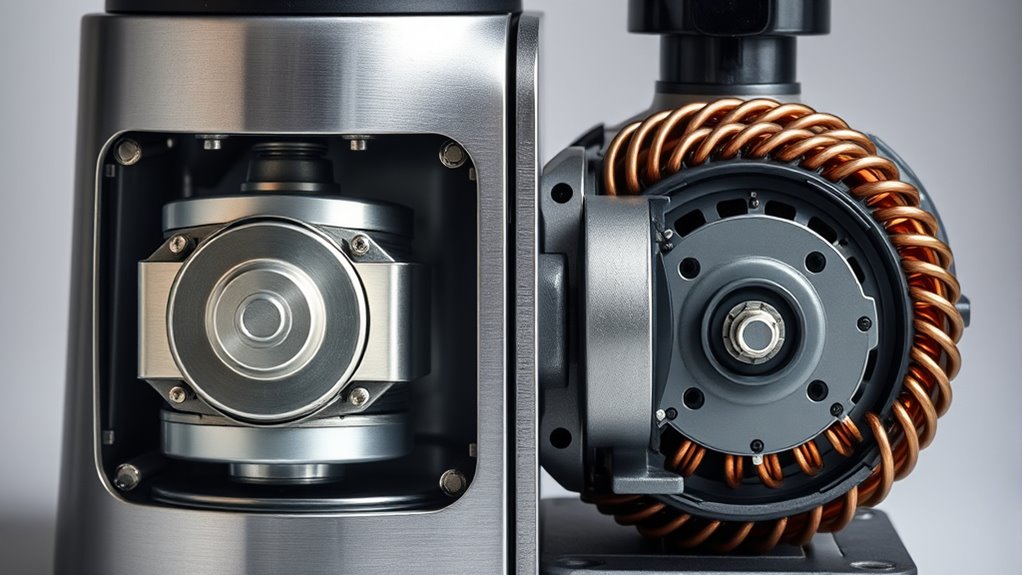
When choosing a food processor, you’ll notice two main motor types: universal and induction. Universal motors are lightweight, deliver high speeds quickly, and work well for small tasks but need regular maintenance due to brushes. Induction motors are more durable, quieter, and handle heavy, continuous processing with steady torque. Understanding their differences helps you pick the right model for your needs—continue exploring to see how each motor impacts your kitchen performance.
Key Takeaways
- Universal motors offer high RPMs and quick starts, ideal for light to medium tasks like chopping and blending.
- Induction motors provide steady torque, making them better suited for heavy-duty, continuous processing such as kneading.
- Universal motors are lighter, more compact, but require regular maintenance due to brushes and commutators.
- Induction motors are more energy-efficient, durable, and operate more quietly, with fewer wear parts.
- Matching motor type to processing needs ensures optimal performance, efficiency, and appliance longevity.
Overview of Motor Types in Food Processors
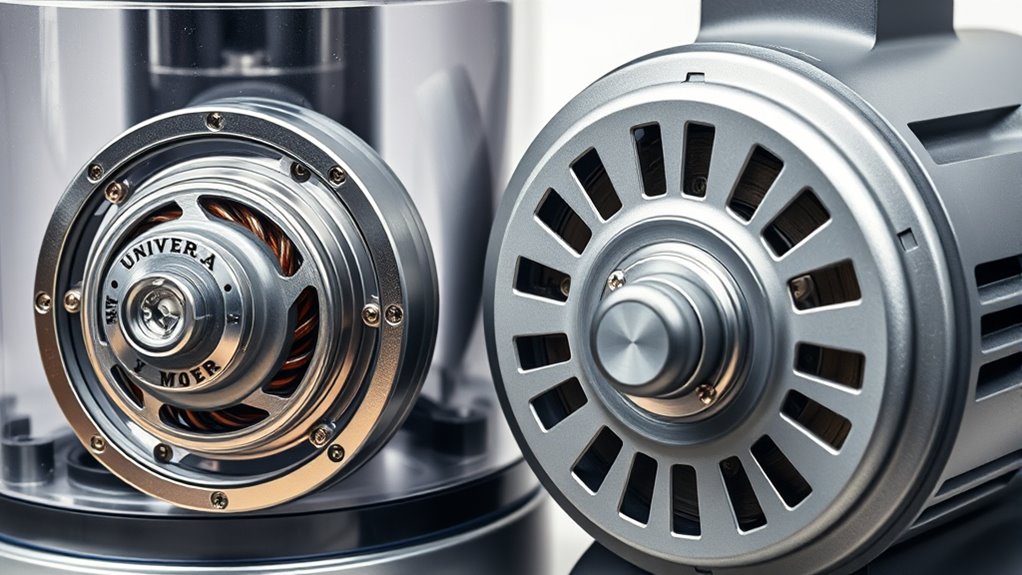

Food processors rely on electric motors housed in their bases to power the blades and disks used for chopping, slicing, shredding, pureeing, and kneading. The motor’s size and power depend on the tasks you want to perform, ranging from about 400 watts for simple jobs to over 1000 watts for heavy-duty work like dough kneading. Stability comes from the motor’s weight and design, preventing movement during operation. Safety features, such as interlocks, ensure the motor only runs when the bowl and lid are securely in place. Additionally, motors must handle variable speeds and maintain consistent torque to process different food textures effectively. Motor durability and maintenance requirements vary depending on the type, influencing long-term performance and reliability. Understanding these motor types helps you choose the right processor for your needs, balancing power, durability, and safety. Considering motor efficiency can also impact energy consumption and overall operation costs.
Characteristics of Universal Motors

Universal motors are a popular choice in food processors because of their versatility and high-speed capabilities. They run on both AC and DC power supplies without modification, reaching speeds up to 32,000 RPM. Their high power-to-weight ratio allows for a compact, lightweight design, perfect for demanding tasks like grinding and mixing. These motors contain brushes and a commutator, making them simple and low-cost but requiring periodic maintenance. Their speed varies widely with load, controlled by voltage or current. Additionally, their simple construction makes them easy to repair and service, which is beneficial for long-term use. Proper maintenance practices are essential to ensure their longevity and optimal performance.
Here’s a visual to help you imagine their components:
| Part | Function | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Brushes & Commutator | Facilitate current reversal | Wear over time, require replacement |
| Rotor (Armature) | Creates torque | Series-connected winding |
| Stator Windings | Generate magnetic field | Connected in series |
| Cooling System | Prevent overheating | Heat dissipation needed |
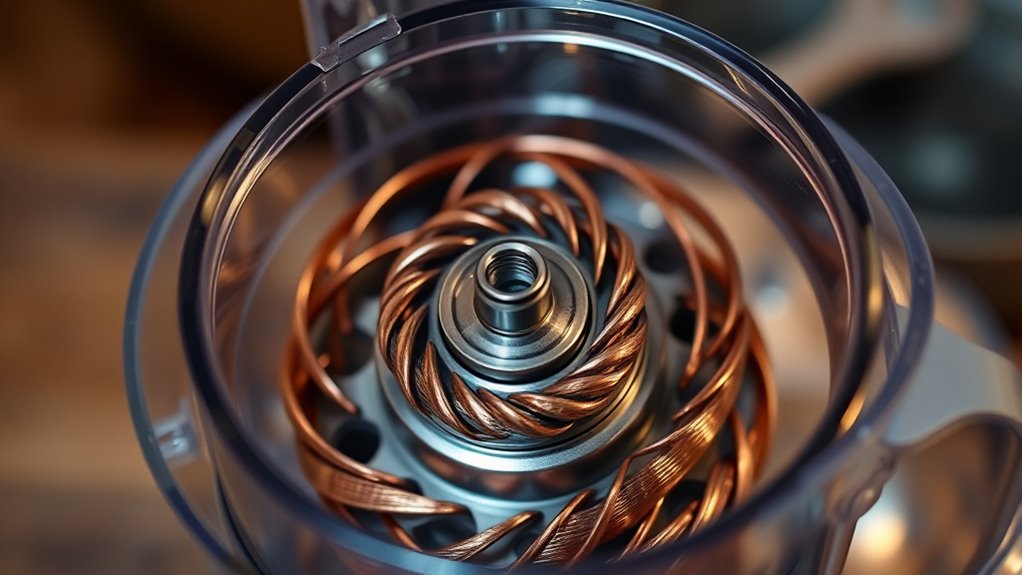
Features of Induction Motors
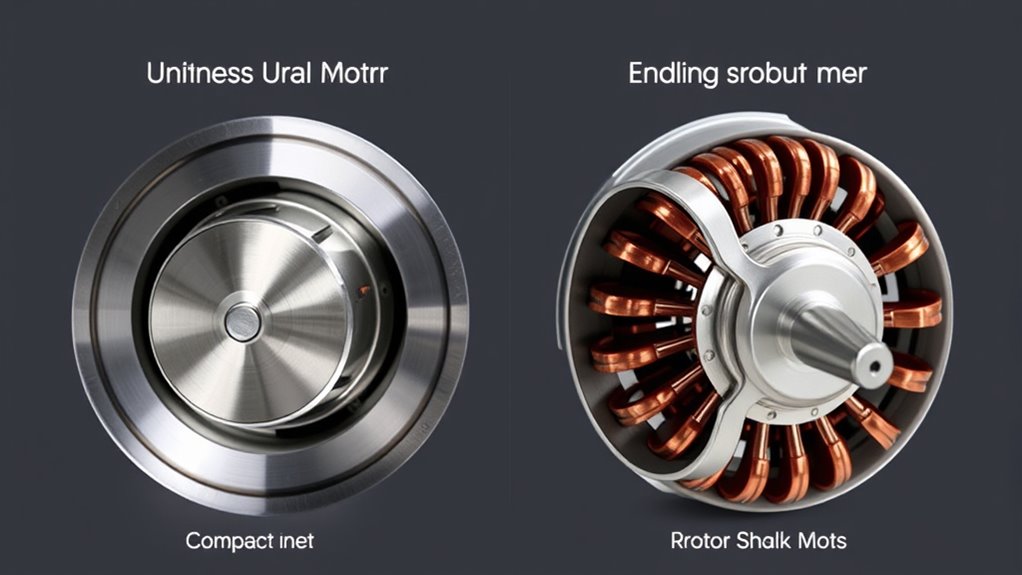
Induction motors stand out for their exceptional durability and long service life, making them a reliable choice in food processors. They typically feature fewer wear parts since they lack brushes, reducing maintenance and increasing longevity. Built to withstand continuous heavy use, they’re suitable for both professional and home kitchens, and generally run cooler than universal motors, which helps prevent overheating. These motors are highly energy-efficient, often earning top energy ratings like A+++, thanks to automatic power adjustments that optimize consumption based on load. They operate quietly, producing about 50 dB, with minimal vibrations, ensuring stable performance and protecting delicate ingredients. Their construction with durable materials like stainless steel enhances heat dissipation, supporting safe, long-term operation in demanding food processing tasks. Brushless design further contributes to their longevity and low maintenance requirements. Additionally, their energy efficiency not only reduces electricity costs but also aligns with environmentally conscious practices.
Comparing Power and Performance Capabilities

When choosing a food processor, understanding the differences in power output and torque is essential. Universal motors deliver high RPMs and quick starts but tend to be less efficient for continuous use, while induction motors provide steady torque and better efficiency over time. By comparing these capabilities, you can select a motor that best matches your processing needs and workload demands. Additionally, Kia Tuning techniques such as ECU remapping and performance upgrades exemplify how different motor types can be optimized for specific performance goals.
Motor Power Range
Motor power range plays a crucial role in determining a food processor’s performance and suitability for various tasks. Higher wattage motors handle dense or tough ingredients more efficiently, reducing strain and processing time. Lower-powered models, typically between 370 to 560 watts, are ideal for basic tasks like chopping and pureeing soft foods. Medium-power units (560 to 1125 watts) offer a good balance for versatile use, tackling medium textures and larger quantities. High-power models (1125 to 2000 watts) excel at heavy-duty tasks like kneading dough or processing large batches. Consider these points:
- Power influences task complexity and batch size
- Higher wattage provides better efficiency and durability
- Lower wattage suits light, occasional use
- Motor durability can help you understand how well different motors withstand prolonged use and heavy loads.
Choosing the right range depends on your typical food prep needs and frequency.
Torque and Speed Control
Universal motors deliver higher starting torque, enabling food processors to quickly engage blades and cut through tough ingredients at startup. This high torque is ideal for tasks requiring rapid acceleration, especially when handling dense or fibrous materials. However, their speed can fluctuate under load, which may affect processing consistency. They can run at very high speeds—up to 25,000 rpm—and their speed control is flexible through voltage adjustments or pulse-width modulation, allowing precise control. In contrast, induction motors provide smoother, more stable torque and operate at lower speeds, typically around 5,750 rpm. They handle continuous loads better, with less performance variation under changing conditions. Although induction motors are less flexible in speed control, their efficiency and steadiness make them suitable for steady, long-term processing tasks. Additionally, motor durability is an important consideration, as induction motors generally have a longer lifespan due to their simpler design and fewer wear-prone parts.
Durability and Longevity Factors
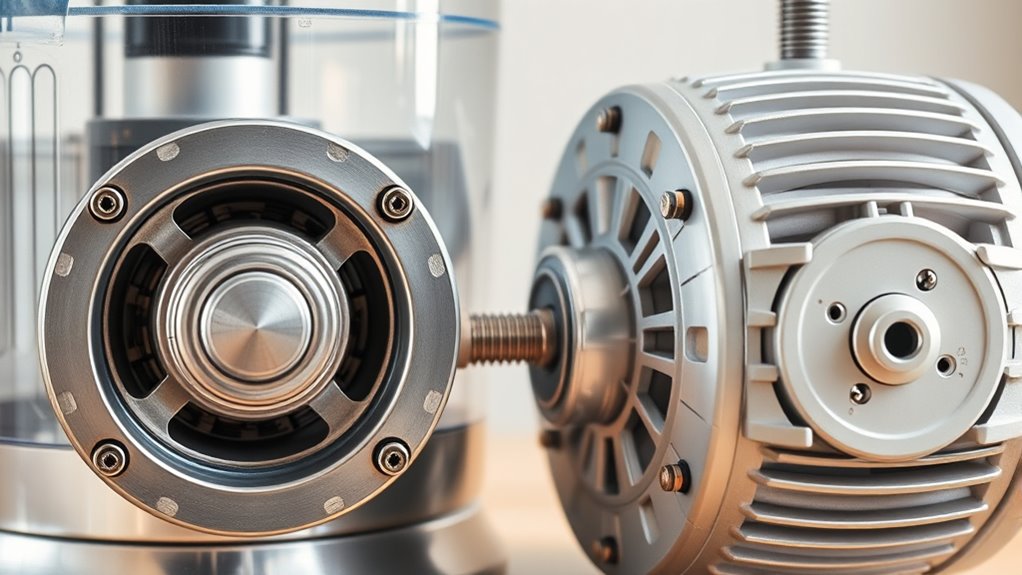
The durability and longevity of a food processor’s motor depend heavily on its construction, type, and how it’s maintained. Induction motors, with their brushless design, experience less mechanical wear and often last thousands of hours, especially with proper cooling. Universal motors, while lighter and cheaper, tend to wear out faster due to brushes and commutators subject to friction. Excessive heat accelerates insulation breakdown in universal motors, shortening their lifespan. Proper maintenance, including cooling and avoiding overloading, is vital for both types. To maximize longevity, consider these factors:
Proper maintenance and cooling extend a food processor motor’s lifespan significantly.
- Regularly inspect and replace brushes in universal motors
- Ensure adequate cooling and ventilation
- Avoid overloading or continuous heavy use
- Proper cooling methods can significantly extend motor lifespan and ensure consistent performance. Maintaining optimal operating temperatures helps prevent premature failure and prolongs overall motor durability.
These practices help extend your motor’s operational life and maintain peak performance.
Suitability for Different Processing Tasks

Choosing the right motor type depends on the specific processing tasks you want to accomplish. If you need quick, light, or medium tasks like blending smoothies or chopping vegetables, a universal motor works well due to its high speed and quick start. It handles short bursts effectively but isn’t ideal for prolonged use. Conversely, induction motors excel in tasks requiring steady power and resistance, such as kneading dough, shredding hard vegetables, or grinding nuts. They provide consistent torque over longer periods, making them suitable for continuous, heavy-duty processing. For delicate tasks like emulsifying or whipping, induction motors offer quieter, smoother operation, minimizing damage to sensitive ingredients. Additionally, motor efficiency is an important factor to consider to ensure energy savings and prolonged appliance lifespan. Properly maintaining your motor can also extend its operational lifespan and ensure consistent performance. Match your processing needs with the motor’s characteristics to guarantee peak performance and efficiency.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Motor Type

Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each motor type helps you choose the right food processor for your needs. Universal motors offer high power and flexibility but need more maintenance, while induction motors are efficient and quiet but bulkier and less versatile. By weighing these factors, you can select a motor that best balances performance, durability, and convenience. Additionally, considering maintenance requirements is essential when choosing between these motor types. Since power consumption varies between motor types, it can also impact your overall energy costs and efficiency.
Universal Motor Pros & Cons
Universal motors are popular in food processors because they offer a combination of high power and versatility. They can run on both AC and DC power, making them adaptable to various kitchen setups. With a high power-to-weight ratio, these motors deliver strong performance without adding bulk. They excel at providing high starting torque, ideal for tasks like kneading dough or chopping tough ingredients. Their easily controllable speed range supports different processing needs, and their lightweight, compact design enhances portability and ease of integration. However, they have some drawbacks:
- Require regular maintenance due to brush and commutator wear
- Generate more noise and vibration during operation
- Have a shorter lifespan compared to brushless motors
Despite these limitations, their cost-effectiveness and performance make them a common choice for versatile, portable food processors.
Induction Motor Strengths & Limits
Are induction motors the best choice for your food processor? They excel in efficiency and durability, converting electricity into mechanical power with less energy use and lasting longer due to their rugged design. They run cooler, reducing overheating risks, and operate quietly with minimal vibrations—ideal for home kitchens. Their steady torque handles heavy loads like dense vegetables or dough, making them reliable for tough tasks. Additionally, motor design innovations continue to improve their performance and adaptability for various kitchen appliances. They are also known for reliability, which is crucial in commercial and home settings, ensuring consistent operation over time. However, induction motors have limitations. They’re more expensive, heavier, and lack variable speed controls, restricting precision. Their slower startup speed may delay quick prep tasks. Plus, they can’t run on DC power, limiting portability. Despite these limits, their efficiency, safety, and longevity make induction motors a strong choice for demanding, long-term use in food processing.
Choosing the Right Motor for Your Food Processor

Choosing the right motor for your food processor depends on your specific processing needs and the types of ingredients you’ll handle. Consider these factors:
Selecting the right motor ensures efficient processing tailored to your ingredient types and usage frequency.
- Power and torque: Higher power and torque help process tough, fibrous ingredients without stalling.
- Noise and durability: Induction motors run quieter and last longer with less maintenance, ideal for frequent use.
- Speed control: Universal motors offer variable speeds and quick acceleration for tasks like kneading or chopping.
- An induction motor’s water-resistant design can provide added protection against moisture, extending the lifespan of your appliance.
If you need a quiet, long-lasting machine for regular tasks, an induction motor is a smart choice. For versatile, high-torque performance with quick starts, a universal motor works well. Match the motor type to your typical processing demands for ideal results.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Motor Type Affect Noise Levels in Food Processors?
You’ll notice that universal motors tend to be louder because their brushes and commutators create vibrations and electrical noise. Induction motors operate more quietly since they lack brushes, reducing mechanical friction and sparking. If noise matters to you, an induction motor is a better choice, especially in noise-sensitive environments. However, universal motors may offer more power at higher speeds, so consider your needs when choosing your food processor.
Can Universal Motors Be Used for Commercial High-Volume Processing?
Yes, you can use universal motors for high-volume commercial processing, but with limitations. They deliver high starting torque, fast speeds, and are cost-effective, making them suitable for mid-volume tasks like chopping or grinding. However, they wear out faster due to brush contact, generate more heat, and require regular maintenance. If your operation involves continuous, heavy-duty use, induction motors might be a more durable, efficient choice.
What Maintenance Is Required for Induction Motors in Food Processors?
You should regularly inspect your induction motor’s electrical connections and power cables for damage, ensuring safety. Keep the motor clean, removing dust and debris. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for lubrication, using the recommended lubricants, and schedule maintenance to prevent wear. Check seals and hoses for leaks, especially if your processor has heating features. If you notice any irregularities, consult a professional for repairs to keep your induction motor running smoothly and efficiently.
Are Induction Motors More Energy-Efficient Than Universal Motors?
Yes, induction motors are generally more energy-efficient than universal motors, achieving around 90–93% efficiency compared to 75–80%. You’ll notice induction motors waste less energy due to fewer mechanical and electrical losses, such as brush friction. While universal motors offer high starting torque and variable speeds, induction motors save you energy over time, making them better suited for continuous, heavy-duty operations in food processing, reducing energy costs and emissions.
How Do Motor Types Impact Processing Speed and Precision?
You’ll notice that induction motors provide steadier speeds and smoother torque, leading to more precise processing. Universal motors run at higher speeds but can cause vibrations and inconsistency, especially during prolonged use. If you prioritize consistent, high-quality results, induction motors are your best choice. They handle tough ingredients better and maintain performance longer, ensuring you get the most accurate chopping, grinding, or shredding every time.
Conclusion
Choosing between a universal and induction motor depends on your needs. If you want quick, powerful performance like a chariot race, a universal motor’s your guy. For durability and steady operation, induction motors are the way to go—think of them as the trusty steed of food processors. Consider your tasks and preferences carefully, and you’ll find the perfect fit. After all, even a modern kitchen can benefit from a little old-world wisdom!









