By managing the combined power draw of your EV charger and household appliances, you can prevent overloads and guarantee safety. Using load management techniques like smart sensors and dynamic control helps you distribute energy efficiently, avoiding costly trips or damage. Static systems are simpler but less flexible, while dynamic ones adapt to your usage patterns. Confirming your home’s electrical capacity is sufficient is key. Stick around to discover how smart strategies can optimize your home’s energy use effectively.
Key Takeaways
- EV chargers typically draw 3.3–7.7 kW continuously, significantly increasing household load compared to standard appliances.
- Load management balances EV charging and appliance use to prevent circuit overloads and breaker trips.
- Dynamic systems adjust power distribution in real-time, prioritizing critical loads during peak EV charging times.
- Appliances like HVAC and large kitchen devices can be scheduled or controlled to optimize overall energy use.
- Proper load management ensures safe, reliable operation while accommodating EV charging alongside household appliances.
Understanding Residential Power Distribution and Load Clustering

Understanding how residential power distribution works is essential to grasp how your home’s electrical system manages multiple loads. Power from the grid first reaches your home through service lines—overhead or underground—that connect to a distribution transformer. This transformer steps down high voltage to a safe 120/240V suitable for your appliances. Inside your house, the main electrical panel distributes power via circuit breakers, which protect your wiring and devices. Subpanels can be added to handle larger demands or separate circuits for specific areas. Your system also clusters loads into groups—lighting, kitchen appliances, HVAC, etc.—to better manage energy. Distribution transformers help ensure voltage stability and reduce fluctuations, maintaining consistent power quality for your household. Modern systems might include smart load management and distributed generation, but the core idea remains: your home’s electrical architecture guarantees safe, balanced power delivery to all connected loads, supporting efficient load management and energy savings. Additionally, understanding your home’s electrical capacity ensures you avoid overloads and optimize energy use.
Impact of Home EV Chargers on Household Electrical Systems
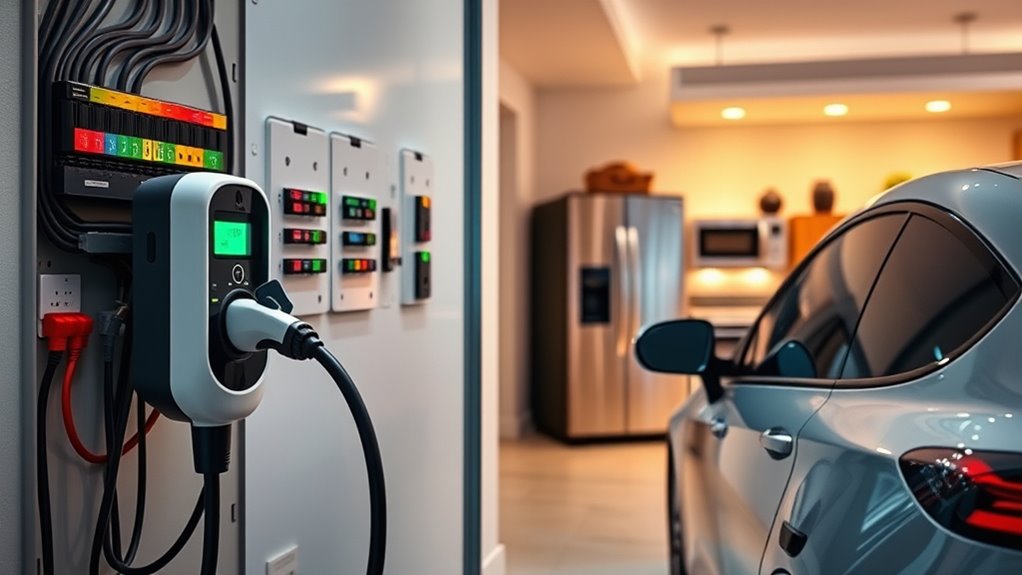

Installing a home EV charger can considerably increase your household’s electrical load, especially when charging at Level 2 speeds that draw between 3.3 and 7.7 kW continuously. This heightened demand can stress your electrical system, particularly if multiple appliances run simultaneously. Here are key impacts to contemplate:
- Circuit Overload Risks: Homes with standard panels may trip breakers if the EV charger runs with heavy appliances like dryers or HVAC systems on the same circuit. Ensuring proper sizing and load distribution is essential to prevent outages. Proper planning can help identify and avoid signs of overload, safeguarding your electrical system.
- Infrastructure Strain: Uncontrolled charging can elevate demand on local feeders, leading to potential upgrades in your neighborhood’s electrical infrastructure.
- Voltage Fluctuations: High concurrent loads might cause voltage drops affecting sensitive electronics and appliances, reducing their lifespan or performance.
- Reliability Concerns: Inadequate load management may also lead to frequent power outages or fluctuations, especially in areas with aging electrical systems that are already fragile.
Proper wiring, dedicated circuits, and smart charging help prevent overloads and maintain system stability.
The Role of Load Management in Balancing Home Power Use

Effective load management is essential for maintaining a balanced and safe home electrical system, especially as more high-demand devices, like electric vehicles and large appliances, are added. By intelligently distributing power across circuits, you prevent overloads and reduce the risk of outages. Prioritization strategies ensure critical appliances, such as heating, cooling, and refrigeration, get power during peak times, improving reliability. Real-time monitoring allows you to make dynamic adjustments, avoiding stress on wiring and electrical components. Load management also promotes safety by reducing frequent circuit breaker trips caused by simultaneous high-demand device use. Incorporating electric heated mattress pads with safety features and proper usage guidelines can contribute to overall home safety and comfort. Plus, it enables you to expand your home’s appliance and EV charging capabilities without costly electrical upgrades, making your system more efficient, resilient, and cost-effective.
Static vs. Dynamic Load Management Techniques

Static and dynamic load management techniques differ markedly in how they distribute electrical power within your home. Static systems assign fixed power levels regardless of real-time needs, making them simple and cost-effective. For example:
- Power is evenly distributed based on preset limits, like 10 kW per charger in a 100 kW setup.
- No sensors or software are needed, reducing complexity and installation costs.
- Best suited for smaller households with predictable, stable energy demands.
In contrast, dynamic load management adapts in real-time, using sensors and software to monitor usage. This approach offers:
- Flexible power redistribution during peak times to maximize efficiency.
- Reduced waste by reallocating unused power.
- Better suited for larger homes or fluctuating energy needs, despite higher initial costs.
Technical Architectures for Home Load Control Systems

Home load control systems rely on a variety of architectural approaches that enable efficient and reliable management of energy consumption. IoT-based smart meters are central, measuring device-level energy use and allowing remote on/off control through communication protocols like SPI. Hierarchical networks connect management, building, and field controllers, coordinating HVAC, lighting, and power with standardized protocols like BACnet. Distributed architectures utilize Single Board Computers (e.g., Raspberry Pi) to scan inputs and control outputs locally, communicating via Ethernet and supporting modular extensions like I2C or ModBus. Open platforms integrate solar PV, energy storage, and smart loads, enabling demand response and forecasting. Incorporating interoperability standards ensures seamless integration across diverse devices and systems, further enhancing overall efficiency. These architectural strategies are essential for achieving load balancing and maximizing energy savings, especially as homes adopt more complex energy systems.
Assessing Household Electrical Capacity Before Installing EV Chargers

Before installing an EV charger, it’s essential to evaluate your household’s electrical capacity to prevent overloads and ensure safe operation. Start by doing a load calculation that includes all your appliances and devices. Consider these key steps:
- Check your electrical panel’s maximum amperage rating, usually marked on the panel label.
- Calculate your current household load, including HVAC, appliances, lighting, and smaller devices.
- Compare your total load with your panel’s capacity, factoring in future needs like additional EVs or appliances.
- Be aware that electrical load management techniques can help optimize your system’s performance and safety.
If your current load is close to or exceeds your panel’s limit, you may need an upgrade. This assessment helps you determine whether your existing system can support an EV charger safely or if upgrades are necessary.
Benefits of Smart Load Management for Home Safety and Efficiency
Smart load management systems play a pivotal role in maintaining electrical safety and optimizing energy use in your household. They detect faults like surges, overloads, and wiring issues in real time, reducing fire risks. Automated circuit tripping prevents damage and hazards during hazardous conditions, while load balancing avoids overheating of panels and wiring, enhancing safety margins. Continuous monitoring alerts you to abnormal usage patterns before hazards develop. Understanding city dynamics is crucial for integrating these systems effectively within your home environment. Integration with smart electrical panels provides a fail-safe, protecting EV chargers and appliances from failures. These systems also improve efficiency by dynamically distributing power, shifting high-demand activities to off-peak hours, and reducing energy costs. Additionally, they coordinate with renewable sources, like solar, and support energy resilience through vehicle-to-home technology, lowering reliance on the grid and extending infrastructure longevity. Incorporating a Gold IRA Rollovers strategy can further secure your long-term financial stability, especially against inflation and economic uncertainties.
Strategies for Integrating Appliances and EV Charging in Residential Settings

Effective integration of appliances and EV charging requires careful planning of your electrical infrastructure to guarantee reliability. To do this, you should focus on:
- Choosing appropriate chargers like Level 2 models with compatible plugs (J1772 or NACS) that fit your home’s existing system without costly upgrades. Incorporating tuning strategies can optimize energy flow and prevent overloads during peak times.
- Strategically placing chargers near electrical panels and parking spots to simplify installation and reduce costs.
- Incorporating renewable energy sources such as solar panels and energy storage to lower grid dependence and better manage overall loads.
- Proper planning can also help prevent potential side effects of overloads, ensuring your system remains safe and efficient during peak usage times.
Additionally, retrofit solutions that work with current panels and appliances are scalable and interoperable. Proper planning ensures safe, efficient, and cost-effective integration of your EV and household appliances.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Can I Determine if My Home Electrical System Can Handle an EV Charger?
You can establish if your home electrical system can handle an EV charger by checking your main panel’s amperage rating and evaluating your current load. Turn off appliances and add their wattage to see if total demand stays within your panel’s capacity. It’s best to consult a licensed electrician who can perform a detailed load calculation and recommend any necessary upgrades to guarantee safe, reliable charging.
What Are the Best Practices for Scheduling Appliance and EV Charging Times?
Think of your home’s electrical system as a symphony—each instrument, or appliance, needs to play at the right time. To keep harmony, schedule EV charging during off-peak hours, like late at night, and avoid simultaneous use of high-power appliances. Use smart chargers and timers to automate this process, prioritizing essential loads first, and defer discretionary cycles when demand is high, ensuring a balanced and safe energy flow.
How Does Load Management Improve Safety During Simultaneous Appliance Use and EV Charging?
Load management improves safety during simultaneous appliance use and EV charging by continuously monitoring your home’s electrical load. It detects overloads or surges and dynamically redistributes power, preventing circuit overloads and breaker trips. This real-time adjustment keeps your wiring safe, reduces fire risks, and guarantees appliances and your EV charge efficiently without damaging your electrical system. By adhering to safety standards, it also minimizes electrocution risks and prolongs your system’s lifespan.
What Are the Differences in Cost and Complexity Between Static and Dynamic Load Management Systems?
You’ll find static load management systems are cheaper to install, costing less upfront due to their simplicity, but they’re less adaptable. Dynamic systems, though more expensive initially because of advanced sensors and software, optimize energy use in real time. Static setups are best for predictable demands, while dynamic ones suit larger or variable loads—offering long-term savings but requiring more technical know-how and maintenance.
Can Renewable Energy Sources Be Integrated Into Home Load Management for EV Charging?
Yes, you can integrate renewable energy sources into your home load management for EV charging. By pairing solar PV systems and battery storage with smart controllers, you can optimize charging times to match renewable generation peaks. Using communication protocols like IEEE 2030.5, you can coordinate between your renewable assets and EV charger, reducing dependency on the grid, lowering costs, and substantially cutting your carbon footprint.
Conclusion
By managing your home’s power wisely, you prevent overloads and guarantee safety—think of it as tending a garden; if you don’t prune regularly, weeds take over. Smart load management balances your appliances and EV charger, saving energy and reducing risks. Embrace dynamic control systems to keep your household running smoothly. Remember, a stitch in time saves nine—addressing load issues early keeps your home safe and efficient for years to come.